Understanding your menstrual cycle for better fertility
A woman’s menstrual cycle is more than a monthly routine—it provides valuable insight into her reproductive health and fertility. Understanding how your cycle works, the hormonal changes involved, and the timing of ovulation can help you maximize your chances of conception and identify potential issues early.
This article explores how understanding your menstrual cycle can improve fertility, what signs to watch for, and practical tips for tracking your cycle effectively.
What Is the Menstrual Cycle?
The menstrual cycle is a monthly process in which a woman’s body prepares for a possible pregnancy. It typically lasts between 21 to 35 days, with an average of 28 days, though variations are normal. The cycle is controlled by hormones, primarily estrogen, progesterone, luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
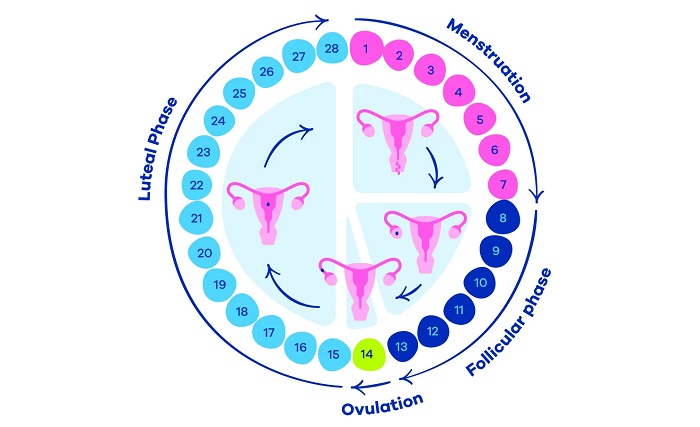
The cycle has four main phases:
- Menstrual Phase (Days 1–5): Shedding of the uterine lining occurs, resulting in menstruation.
- Follicular Phase (Days 1–13): The body prepares an egg for ovulation; estrogen rises, thickening the uterine lining.
- Ovulation (Day 14 in a 28-day cycle): A mature egg is released from the ovary, ready for fertilization.
- Luteal Phase (Days 15–28): Progesterone rises to prepare the uterus for a potential pregnancy; if fertilization does not occur, hormone levels drop, triggering menstruation.
Why Tracking Your Menstrual Cycle Improves Fertility
Understanding your cycle helps identify the fertile window, the days when conception is most likely. Ovulation usually occurs around 12–16 days before the start of your next period. Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days, while an egg is viable for about 12–24 hours.
By tracking your cycle and recognizing ovulation signs, you can time intercourse for the highest chances of conception. Additionally, cycle tracking can help detect irregularities that may indicate fertility issues, such as:
- Irregular or missed periods
- Extremely heavy or painful menstruation
- Short or long cycles beyond the normal range
Signs of Ovulation to Track
Women can use both physical and digital methods to monitor ovulation:
Physical Signs
- Cervical Mucus Changes: During ovulation, cervical mucus becomes clear, slippery, and stretchy—similar to egg whites.
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT): Slight temperature rise (0.4–1.0°F) occurs after ovulation. Tracking BBT daily helps pinpoint ovulation.
- Ovulation Pain: Some women feel mild abdominal cramps or twinges during ovulation.
- Increased Libido: Hormonal changes around ovulation may heighten sexual desire.
Digital and Medical Tools
- Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs): Detect the surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) before ovulation.
- Fertility Apps: Track cycle length, symptoms, and fertile windows.
- Ultrasound Monitoring: Performed by fertility specialists to track follicle development in women with irregular cycles.
How Lifestyle Impacts Your Menstrual Cycle and Fertility
Healthy lifestyle habits can improve menstrual regularity and fertility:
- Balanced Nutrition: Vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats support hormone production.
- Regular Exercise: Moderate activity helps maintain hormonal balance; excessive exercise can disrupt cycles.
- Stress Management: High stress levels can affect ovulation and cycle regularity.
- Healthy Weight: Both underweight and overweight conditions can interfere with fertility.
- Avoid Smoking and Excess Alcohol: These can reduce fertility and affect cycle health.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you’re trying to conceive and notice any of the following, consult a healthcare provider or fertility specialist:
- Irregular cycles lasting less than 21 days or more than 35 days
- Absence of menstruation for several months (amenorrhea)
- Severe menstrual pain or heavy bleeding
- Difficulty tracking ovulation or conceiving after 12 months of trying (6 months if over 35)
Early evaluation can identify conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, or other hormonal imbalances that may affect fertility.
Practical Tips for Tracking Your Menstrual Cycle
- Keep a Calendar: Note the start and end dates of your period each month.
- Monitor Physical Signs: Record cervical mucus, BBT, and ovulation symptoms.
- Use Apps or Devices: Fertility apps or wearable devices can help predict fertile windows more accurately.
- Maintain Consistency: Track your cycle for several months to identify patterns and irregularities.
By combining these methods, you can better understand your cycle, identify fertile days, and increase your chances of conception.
Conclusion
Understanding your menstrual cycle is a powerful tool for improving fertility and reproductive health. Tracking ovulation, monitoring cycle patterns, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle all contribute to optimal fertility outcomes. Women who are proactive in understanding their cycles can make informed decisions, detect potential issues early, and maximize their chances of conceiving naturally.
Being aware of your body and its patterns empowers you to take control of your reproductive health, turning menstrual cycle awareness into a roadmap for fertility success.



